Object Oriented Programming In C++ (CPP) || Programming in C++
Object Oriented Programming In C++ (CPP)
Programming in C++
Introduction to C++
• C++ programming language developed by AT&T Bell Laboratories in 1979 by Bjarne Stroustrup. C++ is fully based on Object Oriented Technology i.e. C++ is ultimate paradigm for the modeling of information.
• C++ is the successor of C language.
• It is a case sensitive language.
Character Set- Set of characters which are recognized by c++compiler i.e Digits (0-9), Alphabets (A-Z & a-z) and special characters + - * , . “ ‘ < > = { ( ] ) space etc i.e 256 ASCII characters.
Tokens- Smallest individual unit. Following are the tokens
• Keyword- Reserve word having special meaning the language and can’t be used as identifier.
Identifiers-Names given to any variable, function, class, union etc. Naming convention (rule) for writing identifier is as under:
i. First letter of identifier is always alphabet.
ii. Reserve word cannot be taken as identifier name.
iii. No special character in the name of identifier except under score sign ‘_’.
Literals-Value of specific data type assign to a variable or constant.
Four type of Literals:
i. Integer Literal i.e int x =10
ii. Floating point Literal i.e float x=123.45
iii. Character Literal i.e char x= ‘a’, enclosed in single quotes and single character only.
iv. String Literal i.e cout<< “Welcome” , anything enclosed in double quotes
Operator – performs some action on data Arithmetic(+,-,*,/,%)
Assignment operator (=)
Increment / Decrement (++, --)
Relational/comparison (<,>,<=,>=,==,!=).
Logical(AND(&&),OR(||),NOT(!).
Conditional (? :)
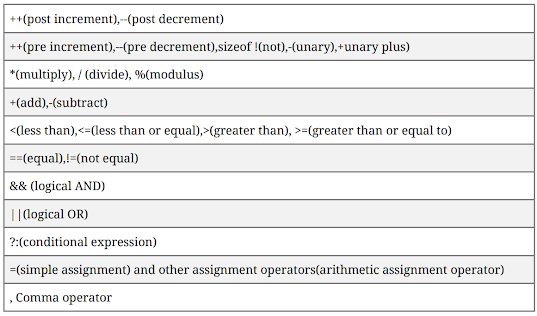
Precedence of Operators:
Punctuation – used as separators in c++ e.g. [ { ( ) } ] , ; # = : etc



Comments
Post a Comment