NCERT solution class 10 Science Chapter 7 || Control and Coordination Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 7 || Control and Coordination Solution || Biology || Science ||
Ques 1: Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin.
Ans 1:
(d) Cytokinin is a hormone present in plants.
Ques 2:
The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) axon.
(b) synapse.
(c) dendrites.
(d) impulse.
Ans 2:
(b) The gap between two neurons is known as synapse.
Ques 3:
The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking.
(b) regulating the heart beat.
(c) balancing the body.
(d) all of the above.
Ans 3:
(d) The brain is responsible for neuro muscular co-ordination, thinking, regulating the heart beat and balancing the body.
Ques 4:
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Ans 4:
Receptors are sensory structures (organs/tissues or cells) present all over the body. The receptors are either grouped in case of eyes or ears, or scattered in case
of skin.
Functions of receptors:
» They sense the external stimuli such as touch, heat or pain.
» They also triggers an impulse in the sensory neuron which sends message
from the muscles to the spinal cord.
When the receptors are damaged, the external stimuli t transferring signals to the
brain are not felt. For example, suppose a case of damaged receptors, if we accidentally touch any hot object, then our hands might get burnt as damaged receptors cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
Ques 5:
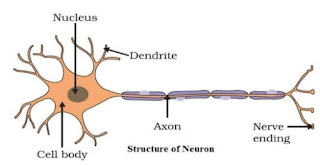
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Ans 5:
Neurons(Nerve cells) are the functional units of the nervous system. The three main parts of a neuron are axon, dendrite and cell body(cyton).
Functions of the three parts of a neuron:
» Axon: It conducts messages away from the cell body.
» Dendrite: It receives information from axon of another cell and conducts
the messages towards the cyton(cell body).
» Cell body (cyton): It contains a nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. It is
mainly concerned with the maintenance and growth.
Ques 6:
How does phototropism occur in plants?
Ans 6:
The movement of plant in response to the light is called phototropism. Stem shows positive phototropism as follows:
When growing plants detect detects light, a hormone called auxin, synthesised at the
shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming to one side of the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from the light. Thus, the plant appears to bend towards the light.
Ques 7:
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Ans 7:
The reflex arc connections between the input and o output nerves meet in a bundle in the spinal cord. In fact, nerves from all over the b body meet in a bundle in the
spinal cord on their way to the brain. In case of any injury to the spinal cord, the signals c coming from the nerves as well as the signals coming to the receptors will be disrupted.
Ques 8:
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Ans 8:
Animals have a nervous system for controlling and coordinating different activities of the body. But plants have neither a nervous system nor muscles.
Plants respond to stimuli by s showing movements. The growth, development, and
responses to the environment in plants is controlled and c coordinated by a special
class of chemical substances known as hormones. These hormones are produced
in one part of the plant body and are translocated to the other needy parts.
For
example, a hormone produced in roots is translocated to other parts where required. The five major types of phytohormone are auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene. These phytohormones are either growth promoters (such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, and ethylene) or growth inhibitors(stops growth) such as abscisic acid.
Ques 9:
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Ans 9:
The maintenance of the body functions in r response to changes in the body by working together of various integrated body systems is known as coordination. All the movements that occur in response to stimuli are carefully coordinated and controlled by the nervous system. In animals, the control and coordination movements are provided by nervous and muscular systems. The nervous system sends m messages to and away from the brain. The spinal cord plays an important role in the relay of thr messages. In the absence of this system of control and coordination, our body will not be
able to function/operate properly.
For example, when anyone accidentally touch a hot utensil, then, he/she immediately withdraw their hand. In the absence of the nerve transmission, we will not withdraw our hand and may get severely burnt.
Ques 10:
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans 10:
Involuntary actions cannot be consciously controlled. For example, we cannot consciously control the movement of food in the a alimentary canal or pumping of of blood through heart. These actions are h however directly under the control of the brain. On the other hand, the reflex actions such as closing of the eyes immediately
when bright light is focused show sudden response and do not involve any thinking. This means that unlike involuntary involuntary actions, the reflex actions are not
under the control of brain.
Ques 11: Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and
coordination in animals.
Ans 11:
Ques 12: What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Ans 12:




Comments
Post a Comment